What is bonito in your mind?
[ 2018.07.20 ]
Bonito is the common name in Scombridae family, but do you really know the bonito? There have 33 bonito species with 106 names in 67 countries and 22 languages. Maybe you are talking about bonito to your partner one day, but are you sure that you are talking about the same bonito?
Let’s display the bonito as below:
Oceanic Bonito
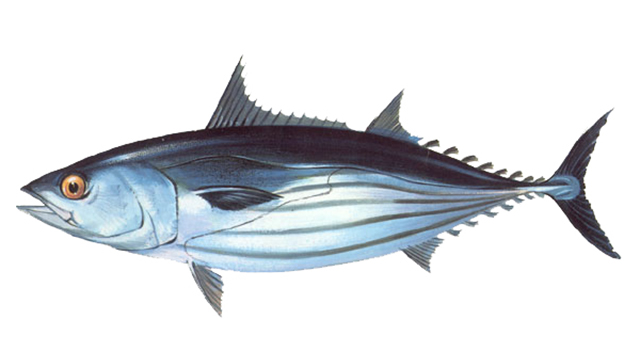
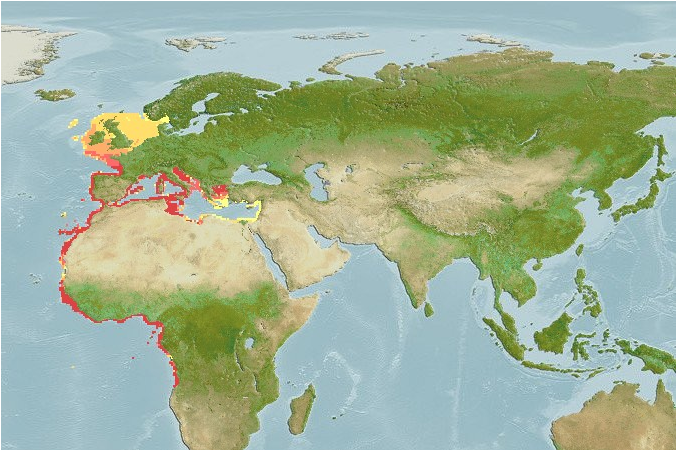
The skipjack tuna (Katsuwonus pelamis) is a medium-sized perciform fish in the tuna family, Scombridae. It is otherwise known as the aku, skipjack tuna ,arctic bonito, mushmouth, striped tuna, Echter Bonito,White bonito,Striped bellied bonito,Okeanskij bonito or victor fish. It grows up to 1 m (3 ft) in length. It is a cosmopolitan pelagic fish found in tropical and warm-temperate waters. It is a very important species for fisheries.
Short description
Dorsal spines (total): 14 - 16;
Dorsal soft rays (total): 14-15;
Anal spines: 0;
Anal soft rays: 14 - 15;
Vertebrae: 41.
Interpelvic process small and bifid. Body without scales except for the corselet and the lateral line. Swim bladder absent. The back is dark purplish blue, lower sides and belly silvery, with 4 to six very conspicuous longitudinal dark bands which in live specimens may appear as continuous lines of dark blotches.
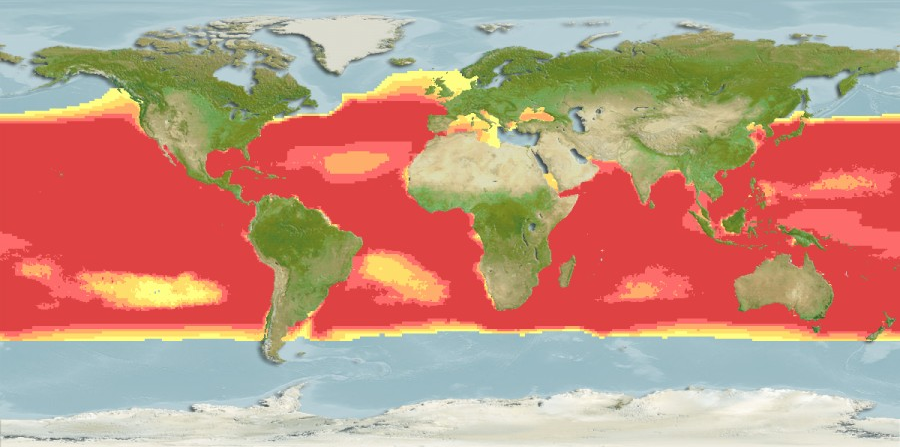
Distribution
Cosmopolitan in tropical and warm-temperate waters. Not found in the Black Sea. Highly migratory species, Annex I of the 1982 Convention on the Law of the Sea.
Striped bonito
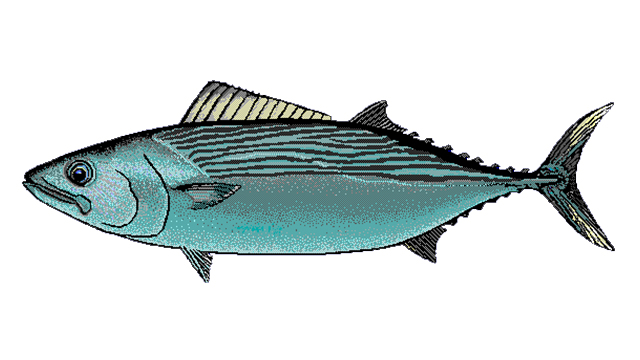
The striped bonito (Sarda orientalis) is a species of marine perciform fish. They have been recorded at lengths of 102 centimetres (40 in), though they are commonly no longer than 55 centimetres (22 in). Distributed through the Indo-Pacific and East Pacific, the striped bonito is known to occur at depths from 1 to 167 metres (3 ft 3 in to 547 ft 11 in).They are called mackerel bonito.
Short description
Dorsal spines (total): 17 - 19;
Anal spines: 0;
Anal soft rays: 14 - 16;
Vertebrae: 44 - 45.
Mouth moderately large. Laminae of olfactory rosette 21 to 39. Interpelvic process small and bifid. Body completely covered with very small scales posterior to the corselet. Swim bladder absent. Spleen large and prominent in ventral view. Liver with elongate left and right lobes and a short middle lobe. Back with narrow oblique stripes.
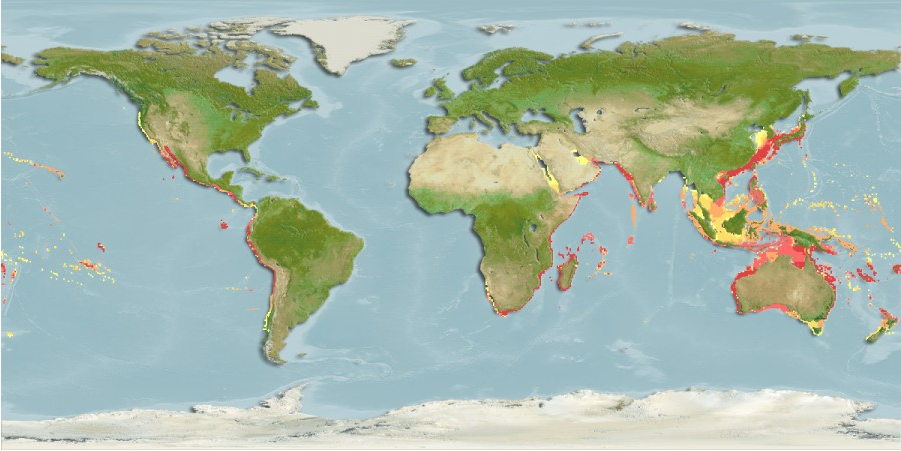
Distribution
Indo-Pacific: widespread but with many gaps in its known distribution. Eastern Pacific: Hawaiian Islands and Pacific coast of USA to southern tip of Baja California and Tres Marias Islands extending to Cabo Blanco, Peru (especially during El Niño events), the Galapagos Islands and Gulf of Guayaquil.
Atlantic bonito

The Atlantic bonito (Sarda sarda) is a large mackerel-like fish of the family Scombridae. It is common in shallow waters of the Atlantic Ocean, the Mediterranean Sea, and the Black Sea, where it is an important commercial and game fish.
Short description
Dorsal spines (total): 20 - 23;
Dorsal soft rays (total): 15-18;
Anal spines: 0;
Anal soft rays: 14 - 17;
Vertebrae: 50 - 55.
Mouth moderately large. Laminae of olfactory rosette 21-39.Interpelvic process small and bifid. Body completely covered with very small scales posterior to the corselet. Swim bladder absent. Spleen large. Liver with elongate left and right lobe and short middle lobe. Oblique dorsal stripes with a greater angle than in other species of Sarda.
Distribution
Eastern Atlantic: Oslo, Norway to Port Elizabeth, South Africa. Also known from the Mediterranean and Black Sea. Western Atlantic: Nova Scotia, Canada to Florida, USA and northern Gulf of Mexico; then from Colombia, Venezuela, and south of the Amazon River to northern Argentina; apparently absent from most of the Caribbean Sea.
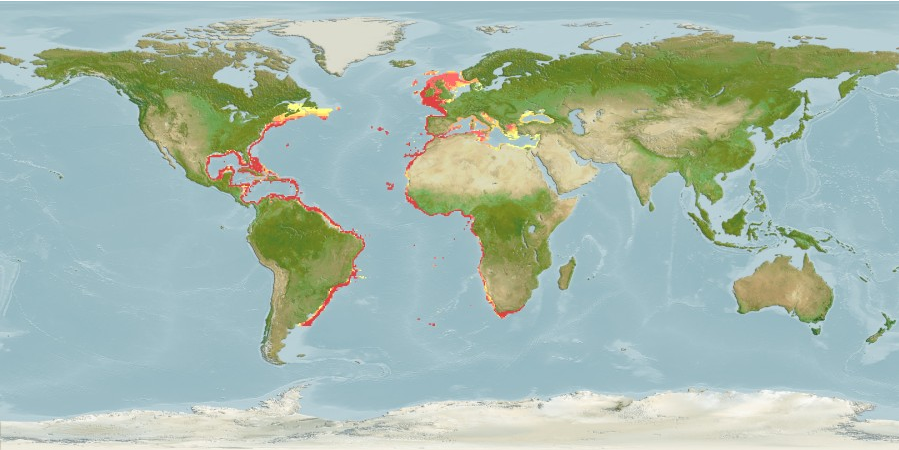
Australian bonito
The Australian bonito, horse mackerel or little bonito, Sarda australis is a fish of the family Scombridae and is found in eastern Australia and New Zealand. They swim at depths reaching depths of approximately 30 m (98 ft), in open water. Its length is commonly at around 40–45 centimetres (16–18 in) fork length and 1.8–2.3 kilograms (4.0–5.1 lb) weight. Its maximum length and weight are about 100 centimetres (39 in) and 9.4 kilograms (21 lb), respectively.
Short description
Dorsal spines (total): 17 - 19;
Dorsal soft rays (total): 13-18;
Anal spines: 0;
Anal soft rays: 14 - 17;
Vertebrae: 45 - 46.
Mouth moderately large. Interpelvic process small and bifid. Swim bladder absent. Laminae of olfactory rosette 21 to 39. Spleen large and prominent in lateral view. Liver with elongate left and right lobes and a short middle lobe. Body completely covered with very small scales posterior to the corselet. Dorsal stripe closer to being horizontal than in other species of Sarda and extending up to the belly in some specimens.
Distribution
Southwest Pacific: southeastern Australia, Norfolk Island and New Zealand.
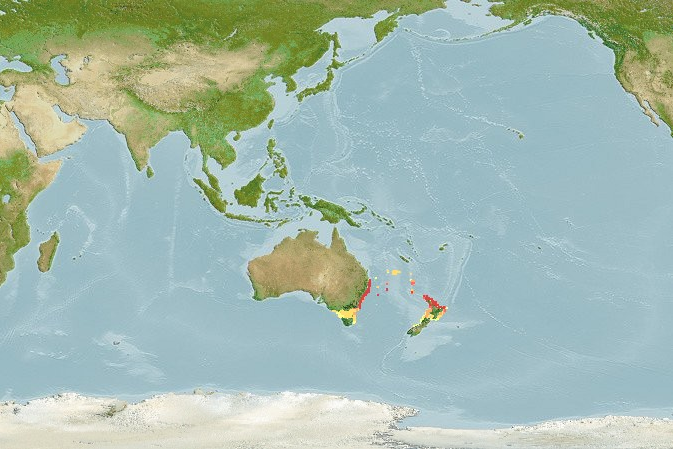
Pacific bonito
Pacific bonito, Sarda lineolata, is a marine species of bonito that is a game fighter but not highly thought of as a food fish. While it has been considered to be a subspecies of Sarda chiliensis, recent treatments recognize it as a species, S. lineolata.
Short description
It is colored blue to violet above, with metallic luster becoming silvery ventrally. It has ten or eleven stripes on its back running obliquely from the dorsum forward, and fifteen or more rakers below the angle on the first gill. The first dorsal fin is contiguous with the second and longer than the head. The caudal peduncle is slender, and the body entirely scaled. It has no teeth on the vomer. It has a small keel on either side of the median keel on the sides of the caudal peduncle, and six to eight finlets on the dorsal and ventral surfaces of the caudal peduncle. The maximum length is about 40 inches and weight 25 pounds. It is found anywhere from inshore to about 100 miles offshore from northern Vancouver Island to Mexico, though it is not normally found north of Point Conception. It usually travels in schools. Fish and squid are its main diet. It is caught by trolling and still fishing, using feather lures, spoons, or live bait.
Distribution
Northeast Pacific: Off the coast of Alaska (60°16'N, 145°32'W) to Cabo San Lucas at the tip of Baja California (22°20'N, 112°27'W) and Revillagigedo Islands.
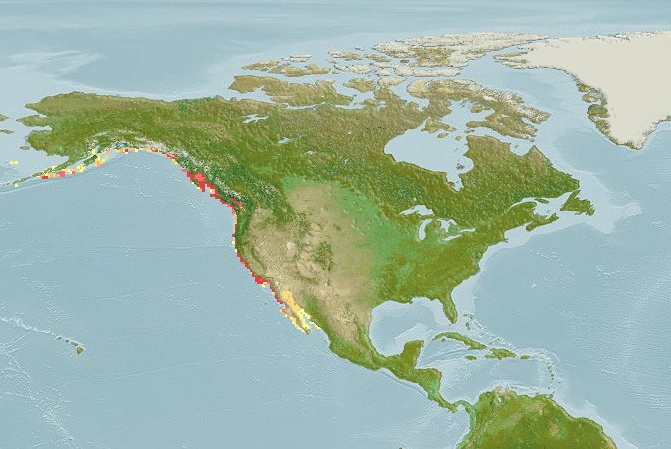
Eastern Pacific bonito
The Eastern Pacific bonito,Sarda chiliensis, is a marine species of bonito. It ranges from Ecuador to Chile. Sarda lineolata, which ranges from Alaska to Mexico has been considered a subspecies, as Sarda chiliensis lineolata, but this treatment renders the species geographically disjunct.
Short description
Dorsal spines (total): 17 - 19;
Anal soft rays: 12 - 15;
Vertebrae: 42 - 46.
Mouth moderately large.Laminae of olfactory rosette 21 to 39. Interpelvic process small and bifid. Swim bladder absent. Spleen large and prominent in ventral view. Liver with elongate left and right lobes and a short middle lobe. Body completely covered with very small scales posterior to the corselet.
Distribution
Southeast Pacific: northern Peru to Talcahuano, Chile (Ref. 9340). The northern subspecies Sarda chiliensis lineolata occurs from off the coast of Alaska, southward to Cabo San Lucas at the tip of Baja California, and in the Revillagigedo Islands.
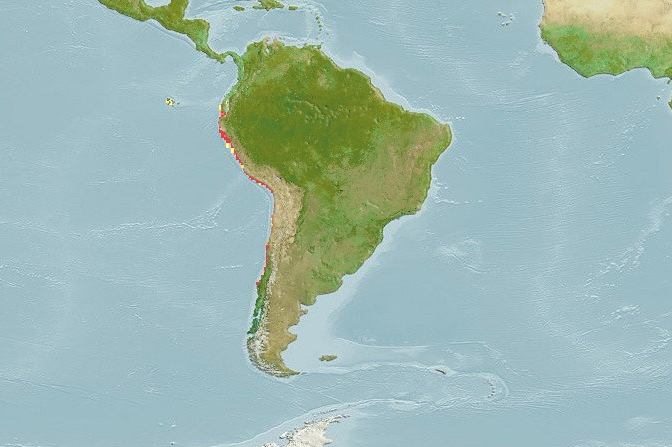
Plain bonito
Orcynopsis unicolor (plain bonito) is a ray-finned, bony fish in the bonito tribe of the mackerel family (Scombridae).
Short description
Dorsal spines (total): 12 - 14;
Dorsal soft rays (total): 12-15;
Anal soft rays: 14 - 16.
Mouth rather large, upper jaw reaching to hind margin of eye. Laminae of olfactory rosette 25 to 28. Interpelvic process small and bifid. Body naked behind the well developed corselet. Swim bladder absent. Vertebrae 17 or 18 precaudal plus 19 to 21 caudal, total 37 to 39. Anterior three quarters of first dorsal fin black.
Distribution
Eastern Atlantic: Oslo, Norway south to Dakar, Senegal but the range is centered in the southern Mediterranean Sea. Not known from Madeira, the Canary Islands or Cape Verde.
Leaping Bonito
The leaping bonito (Cybiosarda elegans) is a species of saltwater finfish from the Scombridae (Mackerel) family. Scombridae includes such tribes as the mackerels, tunas, and bonitos – the latter of which, the Sardini tribe, this fish is a member. It is the only member of the genus Cybiosarda, which is therefore called a monotypic taxon. Since the bonitos and tunas are close relatives, this fish has variously been referred to by such other common names as Australian tuna, striped bonito, and Watson's bonito.
Short description
Dorsal spines (total): 16 - 18;
Dorsal soft rays (total): 17-19;
Anal spines: 0;
Anal soft rays: 15 - 17;
Vertebrae: 45 - 50.
Mouth rather large, upper jaw reaching to hind margin of eye. Laminae of olfactory rosette 28 to 33. Interpelvic process small and bifid. Body mostly naked behind the well developed corselet except for a band of scales along the bases of dorsal and anal fins and patches around the bases of the pectoral and pelvic fins. Swim bladder absent. The back is deep blue, covered with elongate black spots; the belly is light with several stripes like those of the skipjack tuna.
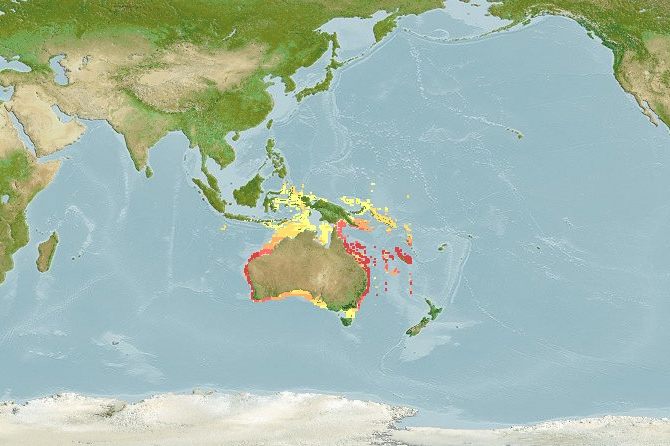
Distribution
Western Pacific: restricted to the northern three quarters of Australia (absent from the south coast) and the southern coast of Papua New Guinea.
Unechter Bonito

In German, Auxis rochei ,Auxis thazard and Sarda sarda are called Unechter Bonito. Let's make a distinction because Auxis thazard is a common fishery resource with relatively good yield and high commercial value.
The frigate tuna or frigate mackerel, Auxis thazard, is a species of tuna, in the family Scombridae, found around the world in tropical oceans. The eastern pacific population is now regarded as a separate species by some authorities, Auxis brachydorax.
Short description
Dorsal spines (total): 10 - 12;
Dorsal soft rays (total): 10-13;
Anal spines: 0;
Anal soft rays: 10 - 14.
Back bluish, turning to deep purple or almost black on the head. A pattern of 15 or more narrow, oblique to nearly horizontal, dark wavy lines in scaleless area above lateral line. Belly white. Pectoral and pelvic fins purple, their inner sides black. Body robust, elongate and rounded. Teeth small and conical, in a single series. Pectoral fins short, but reaching past vertical line from anterior margin of scaleless area above corselet. A large single-pointed flap (interpelvic process) between pelvic fins. Body naked except for the corselet, which is well developed and narrow in its posterior part (no more than 5 scales wide under second dorsal-fin origin). A strong central keel on each side of caudal-fin base between 2 smaller keels .
Distribution
Atlantic, Indian and Pacific (Western Central). Eastern Pacific population recognized as subspecies Auxis thazard brachydorax . Many authors have used the name Auxis thazard as including Auxis rochei in the belief that there was only a single worldwide species of Auxis.Highly migratory species.
List of detailed classification of the above species
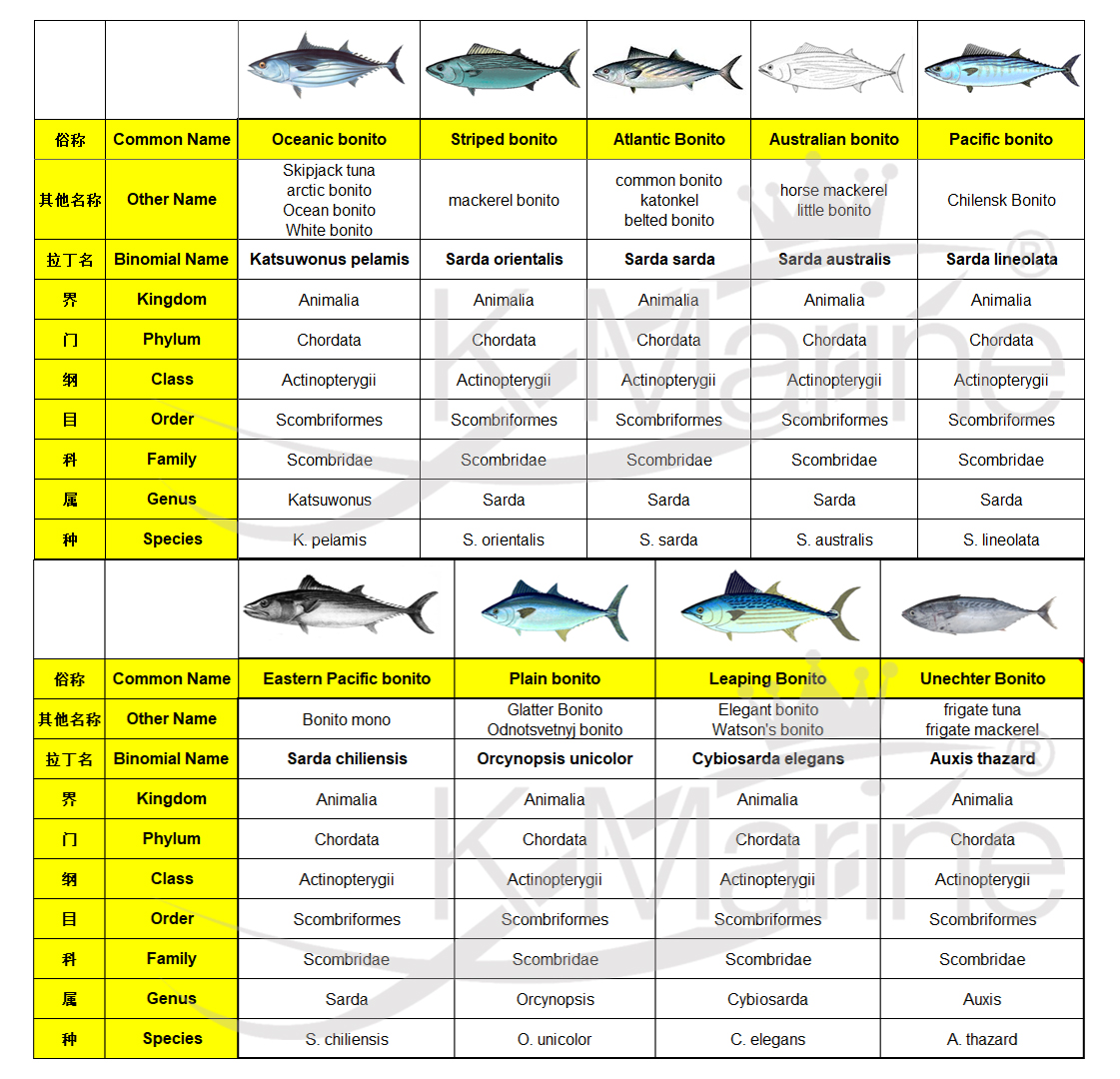
Did you read the above description and learn more about bonito? Remember that Latin Name is the unique name. The common name corresponding fish is not mentioned above in some countries and regions, here we just statistics compiled some people have relatively identity.
Welcome to leave messages to tell us what we did not mention or what you call the fish in different name at your side, waiting for you to share.



